Banana River: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (160 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
< | <div class="irlbody irlbow"> | ||
{{ | {{IRL header estuary|cat=Banana River}} | ||
| | <div class="irlcontenttop"> | ||
[[File:Banana_River_KSC_Aerial.jpg|320px|thumb|right|alt=Aerial photo of Banana River lagoon at Kennedy Space Center.|Banana River at KSC]] | |||
[[Banana River]] (''"Ulumay Lagoon"'') is a 31 mile long brackish water lagoon that lies between Titusville and Indian Harbour Beach in Brevard County, Florida. At 30,000 acres, Banana River is the smallest lagoon in the [[Indian River Lagoon Estuary|Indian River Lagoon National Estuary]]. | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
Banana River lagoon is bounded by Merritt Island on the west and by Brevard's barrier island to the east. The lagoon's northern boundary lies within Kennedy Space Center (KSC) and the southern end merges with the [[Indian River]] at Dragon Point in Indian Harbour Beach. | |||
Northern Banana River is jointly administered by KSC and the [[United States Fish and Wildlife Service|U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS)]] as part of the [[Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge]]. FWS maintains a No-Motor Zone on the lagoon between the KSC property line and the Beachline Expressway (SR528).<ref name="fwsfish" /> There is no public access allowed north of the KSC property line. | |||
== | Banana River is recognized as an ''"Outstanding Florida Water"'' and overseen by the [[Florida Department of Environmental Protection|Florida Department of Environmental Protection (FDEP)]]. FDEP manages most of the lagoon south of the Beachline Expressway (SR528) as the [[Unit:Banana River Aquatic Preserve|Banana River Aquatic Preserve]].<ref name="BRLMAP2016" /> | ||
[[File:Merritt Island_Dragons_Point.jpg|320px|thumb|right|alt=The southern end of Banana River lagoon is at Dragons point in Merritt island.|Banana River Southern Terminus at Dragon Point, Merritt Island]] | |||
600 acres of Sykes Creek, a Banana River tributary, are preserved by Brevard's [[Unit:Brevard County Environmentally Endangered Lands Program|Environmentally Endangered Lands Program]] as the [[Unit:Ulumay_Sanctuary|Ulumay Sanctuary]]<ref name="ulumay" /> and 300 acres in Cocoa Beach are preserved as the [[Unit:Thousand Islands Conservation Area|Thousand Islands Conservation Area]]. | |||
With an average 4ft depth, the Banana River Lagoon's shallow ecosystem includes numerous salt marshes, [[mangrove]] swamps, [[seagrass]] beds, oyster bars, mudflats, and spoil islands, that provide habitat for many [[:Category:Biota|animal and plant species]]. | |||
Banana River is an important spring habitat (300-500 individuals/survey day)<ref name=fdepbr /> for the [[West Indian Manatee|West Indian manatee]], with many living in the lagoon year-round. The lagoon also supports the largest pelican rookery on the Atlantic Coast<ref name="fdepbr" /> and a significant population of [[Bottlenose dolphin|Atlantic Bottlenose dolphin]]. | |||
Commercial and recreational activities in the Banana River lagoon are estimated to generate more than $800 million annually for the local economy. | |||
In 2016 a Banana River algae bloom caused massive fish kills from Cape Canaveral to Indian Harbor Beach. Green algae and dead marine life were common scenes along the lagoon. | |||
==Water Body== | |||
{{Map Embed|coord=28.458480,-80.624358|zoom=10}} | |||
<span style="font-size:0.85em">Location: 28°27'30.5"N, 80°37'27.7"W | |||
<br/>GIS: 28.458480,-80.624358</span> | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:330px; overflow:auto;padding-top:20px"> | |||
<div class="irlcollapsetitle">Banana River Tributaries</div> | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | |||
<div class="irlcollapsetext">Tributaries are listed from North to South.</div> | |||
<div>{{#section:Water Body List|bananariverwater}}</div> | |||
</div></div> | |||
[[Info:Banana Creek|Banana Creek]] connects Banana River lagoon to the [[Indian River|Indian River lagoon]] south of [[Max Brewer Bridge]] (SR404) in Titusville, Florida. A short distance south, Banana Creek enters Kennedy Space Center (KSC) property and dead ends at KSC's Saturn Causeway. | |||
Banana River lagoon was originally a continuous waterway between Merritt Island and Cape Canaveral until 1964 when the construction of NASA's Saturn Crawlerway causeway split the lagoon in two. | |||
South of Saturn Causeway, Banana River ranges through Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Space Force Station property to the Beachline Expressway (SR528) causeway. | |||
At Port Canaveral, the lagoon connects to the Atlantic Ocean via [[Canaveral Lock]]s and to the Indian River via [[Canaveral Barge Canal]]. | |||
[[Info:Sykes Creek|Sykes Creek]], in central Merritt Island, connects to the Banana River south of SR520 in Cocoa Beach. | |||
Banana River ends at Dragon's Point, the southern tip of Merritt Island, where it joins the [[Indian River|Indian River lagoon]] at Indian Harbour Beach. | |||
Article: [[:Category:Banana River Water Body|Banana River Water Body]] | |||
<div style="width:100%;float:left"> | |||
[[File:Banana River Dragons Point 04.jpg|320px|thumb|left|alt=Banana River at Dragons Point.| Banana River at Dragons Point.]] | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:330px; overflow:auto;padding-top:20px"> | |||
<div class="irlcollapsetitle">Banana River Bridges</div> | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | |||
<div class="irlcollapsetext">Bridges are listed from North to South.</div> | |||
<div>{{#section:Bridge List|bananariverbridgelist}}</div> | |||
</div></div> | |||
There are seven causeway bridges bisecting the 31 mile long Banana River lagoon. Each earthen berm causeway impedes water movement and reduces the lagoon's ability to flush. | |||
Article: [[:Category:Banana River Bridges|Banana River Bridges]] | |||
==Water Quality== | |||
[[File:Port-Canaveral-Super-Bloom.jpg|320px|thumb|right|alt=Aerial photo of the Banana River algae superbloom at Port Canaveral in 2016.|2016 Banana River Superbloom]] | |||
Like the rest of the IRL estuary, the Banana River lagoon suffers from [[Nutrient Pollution|nutrient pollution]] due to human impact. Stormwater runoff, faulty sewer systems, and septic tanks, over-fertilized lawns, and excessive development over wetland areas have greatly increased the residual levels of nitrogen and phosphorus in the water. | |||
Algae thrive on the excess nutrients, grows rapidly until it clouds the water, which blocks the sunlight and kills the [[seagrass]] beds. The blooming algae also cause a lack of oxygen in the water which in turn kills the marine animals. | |||
DEP's Banana River Lagoon Basin Management Action Plan<ref name="DEPBRLBMAP2013" /> presents a long-term plan to restore [[seagrass]] habitats in the Indian River Lagoon Basin through the reduction of watershed loadings of total nitrogen and total phosphorus. | |||
[[File:KSC_Banana_River_Seagrass_Loss_graph.jpg|320px|thumb|right|alt=Banana River Seagrass Coverage Chart.|Banana River Seagrass Coverage Chart.]] | |||
Excerpt from DEP's Banana River Lagoon Progress 2016 Review: | |||
"In 2011, an algal super bloom occurred in the Banana River Lagoon (BRL) and North IRL, with a separate bloom affecting part of the Central IRL. A brown algal bloom affected much of the IRL during 2012. The full impact to seagrasses from these blooms will not be known for a number of years, but there are documented losses of seagrasses in the BRL linked to the blooms. Research is underway to understand the causes of these blooms; however, they appear to be due, in part, to legacy loads in the lagoon from past nutrient discharges. Removing the sources of nutrients from the lagoon’s watershed will help remediate the legacy load."<ref name="BRLBMAP2016Rev" /> | |||
The Banana River Lagoon Basin Management Action Plan (BMAP) is currently undergoing review and revision for a 2021 adoption.<ref name="DEPBRLBMAP2020" /> | |||
Article: [[Banana River Water Quality]] | |||
==Restoration== | |||
The 2016 DEP Banana River Lagoon BMAP Progress Report list's many completed and ongoing projects, including stormwater retention systems, stormwater filters, sewer system repairs, and water quality monitoring.<ref name="BRLBMAP2016Rev" /> | |||
In January 2019 a $2.8 million stormwater and septic conversion project began in Merritt Island. It funded the installation of a new sewer main enabling the conversion of 23 commercial septic tanks and 60 residential septic tanks that were leeching effluent into the lagoon. | |||
The 2019 project also funded the installation of stormwater pipelines that diverted stormwater runoff to retention filtering ponds instead of flowing directly to the river.<ref name="SJRWMDBRL" /> | |||
==Organization== | |||
[[File:Banana_River_Organizational Chart.png|320px|right|thumb|alt=Tap the photo to view an interactive Banana River Organizational Chart.|Tap for [[Banana River Lagoon Organizational Chart]]|link=Banana River Lagoon Organizational Chart]] | |||
As of 2021 there are approximately fourteen federal, state and county government organizations working within the Banana River lagoon watershed. | |||
Florida's Department of Environmental Protection monitors water quality and sets environmental standards. Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission protects fish, wildlife and habitats, and enforces the law on the water. St. Johns River Water Management District and Brevard County's Save Our Indian River Lagoon Program have worked together on many Banana River restoration projects. | |||
* Interactive chart: [[Banana River Lagoon Organizational Chart]] | |||
* Full size image: [[Media:Banana_River_Organizational_Chart.jpg]] | |||
Article: [[Banana River Lagoon Organization]] | |||
==History== | |||
[[File:Banana River Night Launch 320.jpg|320px|thumb|right|alt=Kennedy Space Center night launch over Banana River lagoon.|KSC Night Launch Over Banana River]] | |||
===Banana River Air Station=== | |||
Construction of the Banana River Naval Air Station began in December 1939 and the station was commissioned on 1 October 1940. | |||
The station supported seaplane patrol operations during World War II, a blimp squadron which conducted search and rescue along Florida's east coast, a PBM seaplane pilot training program, and an advanced navigation school. | |||
In 1944 the station consisted of 391 officers, 2492 enlisted, and 587 civilians. The number of aircraft present on the base, including F6 Hellcats and O52U Kingfishers, reached a high of 228. | |||
[[File:Ares I-X Return to KSC 1.jpg|320px|thumb|right|alt=Ares I-X Returns to KSC|Ares I-X Returns to KSC]] | |||
The station continued to operate as a Navy support base for two years after the war, but the installation was deactivated on 1 August 1947.<ref name="brnas" /> | |||
===Patrick Space Force Base=== | |||
The Navy transferred the station to the Air Force on 1 September 1948 and it was renamed the Joint Long Range Proving Ground (JLRPG). On 1 August 1950, it was renamed Patrick Air Force Base in honor of Major General Mason Patrick. | |||
On December 9, 2020 Patrick Air Force Base was renamed Patrick Space Force Base. Patrick is the headquarters of the 45th Space Wing, the parent organization responsible for operations at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station.<ref name=brnas /> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="irlcontentbottom noprint"> | |||
==Video== | |||
Select a video to play or visit the [https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCHtV0jOmRQMpJEtUXfIjAbA Indian River Lagoon Project YouTube Channel] - [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SPHhIAt8NIc&list=PLCiZ8bCTmnlipGxJ9OVG6bMmfDrRb9oTs Banana River Video Playlist]. | |||
{{#evl:A37f1pMeiAA|Above Banana River at Kelly Park|1|player=youtube}} | |||
<br />{{#evl:fn1mNWIRQHI|Above Banana River at Thousand Islands|2|player=youtube}} | |||
<br />{{#evl:SPHhIAt8NIc|Above Banana River at Sunset|3|player=youtube}} | |||
<br />{{#evl:devxZ0m7X2c|Banana River Fish Kill 2016|4|player=youtube}} | |||
<evlplayer w="340" h="220" id="youtube" style="width:inherit;">https://img.youtube.com/vi/A37f1pMeiAA/0.jpg</evlplayer> | |||
==See Also== | |||
* [[:Category:Banana River Water Body|Banana River Water Body]] | |||
* [[:Category:Banana River Bridges|Banana River Bridges]] | |||
* [[Banana River Water Quality]] | |||
* [[Banana River Lagoon Organization|Banana River Lagoon Organization]] | |||
* [[Banana River Facts]] | |||
==Web Links== | |||
* [https://fdep.maps.arcgis.com/apps/MapSeries/index.html?appid=3113f204a7814a228f0b052262562d01 DEP - Basin Management Plan Story Map] | |||
* [https://floridadep.gov/rcp/aquatic-preserve/locations/banana-river-aquatic-preserve DEP - Banana River Aquatic Preserve] | |||
* [https://www.brevardfl.gov/EELProgram/home Brevard County Environmentally Endangered Lands Program] | |||
* [https://www.fws.gov/refuge/Merritt_Island/Fishing.html.aspx FWS - Banana River No Motor Zone Fishing] | |||
* [https://www.spanishflytv.com/article/urban-nature-banana-river-florida/ SpanishFlyTV - Urban Nature Banana River] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<section begin=References /> | |||
<references> | |||
== | <ref name="fwsfish">[https://www.fws.gov/refuge/Merritt_Island/Fishing.html.aspx FWS Merritt Island Refuge Fishing]</ref> | ||
<ref name="fdepbr">[https://floridadep.gov/rcp/aquatic-preserve/locations/banana-river-aquatic-preserve Banana River Aquatic Preserve]</ref> | |||
<ref name="ulumay">[https://www.brevardfl.gov/ParksRecreation/Central/ParksInMerrittIsland/Ulumay Ulumay Wildlife Sanctuary]</ref> | |||
<ref name="brnas">[http://afspacemuseum.org/displays/BRNAS/ Air Force & Space Museum Banana River Naval Air Station]</ref> | |||
<ref name="BRLMAP2016">[http://publicfiles.dep.state.fl.us/CAMA/plans/aquatic/Indian-River-Lagoon-AP-System-Management-Plan.pdf FDEP 2016 Indian River Lagoon Aquatic Preserves System Management Plan (PDF, 267pp)]</ref> | |||
<ref name="DEPBRLBMAP2013">[https://floridadep.gov/sites/default/files/banana-river-lagoon-bmap.pdf DEP Banana River Lagoon BMAP 2013 (PDF 90pp 1.49MB)], retrieved 2021-01-08</ref> | |||
<ref name="BRLBMAP2016Rev">[https://floridadep.gov/sites/default/files/BRL_BMAP_2016_Progress_Report_0.pdf DEP 2016 Banana River Progress Review]</ref> | |||
<ref name="DEPBRLBMAP2020">[http://publicfiles.dep.state.fl.us/DEAR/BMAP/IndianRiverLagoon/BMAP_Documents/2020_IRL_Updates/Drafts/RevisedDraft_BRL_BMAP_12-16-20.docx DEP - Banana River Lagoon BMAP 2020 Draft (DOCX 137pp 5.6MB)]</ref> | |||
<ref name="SJRWMDBRL">[https://www.sjrwmd.com/2019/01/cost-share-project-to-benefit-banana-river-lagoon-water-quality/ SJRWMD 2019 BRL Stormwater and Septic to Sewer Project]</ref> | |||
</references> | |||
<section end=References /> | |||
</div> | |||
{{IRL footer estuary|cat=Banana River}} | |||
</div> | |||
[[Category:Banana River]] | [[Category:Banana River]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:49, June 2, 2023

Banana River ("Ulumay Lagoon") is a 31 mile long brackish water lagoon that lies between Titusville and Indian Harbour Beach in Brevard County, Florida. At 30,000 acres, Banana River is the smallest lagoon in the Indian River Lagoon National Estuary.
Banana River lagoon is bounded by Merritt Island on the west and by Brevard's barrier island to the east. The lagoon's northern boundary lies within Kennedy Space Center (KSC) and the southern end merges with the Indian River at Dragon Point in Indian Harbour Beach.
Northern Banana River is jointly administered by KSC and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) as part of the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. FWS maintains a No-Motor Zone on the lagoon between the KSC property line and the Beachline Expressway (SR528).[1] There is no public access allowed north of the KSC property line.
Banana River is recognized as an "Outstanding Florida Water" and overseen by the Florida Department of Environmental Protection (FDEP). FDEP manages most of the lagoon south of the Beachline Expressway (SR528) as the Banana River Aquatic Preserve.[2]

600 acres of Sykes Creek, a Banana River tributary, are preserved by Brevard's Environmentally Endangered Lands Program as the Ulumay Sanctuary[3] and 300 acres in Cocoa Beach are preserved as the Thousand Islands Conservation Area.
With an average 4ft depth, the Banana River Lagoon's shallow ecosystem includes numerous salt marshes, mangrove swamps, seagrass beds, oyster bars, mudflats, and spoil islands, that provide habitat for many animal and plant species.
Banana River is an important spring habitat (300-500 individuals/survey day)[4] for the West Indian manatee, with many living in the lagoon year-round. The lagoon also supports the largest pelican rookery on the Atlantic Coast[4] and a significant population of Atlantic Bottlenose dolphin.
Commercial and recreational activities in the Banana River lagoon are estimated to generate more than $800 million annually for the local economy.
In 2016 a Banana River algae bloom caused massive fish kills from Cape Canaveral to Indian Harbor Beach. Green algae and dead marine life were common scenes along the lagoon.
Water Body
Location: 28°27'30.5"N, 80°37'27.7"W
GIS: 28.458480,-80.624358
Brevard
- Banana Creek
- Canaveral Lock
- Canaveral Barge Canal
- Sykes Creek
- Grand Canal
- Indian River
Banana Creek connects Banana River lagoon to the Indian River lagoon south of Max Brewer Bridge (SR404) in Titusville, Florida. A short distance south, Banana Creek enters Kennedy Space Center (KSC) property and dead ends at KSC's Saturn Causeway.
Banana River lagoon was originally a continuous waterway between Merritt Island and Cape Canaveral until 1964 when the construction of NASA's Saturn Crawlerway causeway split the lagoon in two.
South of Saturn Causeway, Banana River ranges through Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Space Force Station property to the Beachline Expressway (SR528) causeway.
At Port Canaveral, the lagoon connects to the Atlantic Ocean via Canaveral Locks and to the Indian River via Canaveral Barge Canal.
Sykes Creek, in central Merritt Island, connects to the Banana River south of SR520 in Cocoa Beach.
Banana River ends at Dragon's Point, the southern tip of Merritt Island, where it joins the Indian River lagoon at Indian Harbour Beach.
Article: Banana River Water Body
Brevard County
- Kennedy Parkway Bridge CR3
- Saturn Causeway
- NASA Parkway Causeway SR405
- Beachline Causeway SR528
- Canaveral Locks Bridge SR401 (info)
- Hubert Humphrey Bridge SR520
- Pineda Causeway SR404 (info)
- Mathers Bridge CR3 (info)
There are seven causeway bridges bisecting the 31 mile long Banana River lagoon. Each earthen berm causeway impedes water movement and reduces the lagoon's ability to flush.
Article: Banana River Bridges
Water Quality

Like the rest of the IRL estuary, the Banana River lagoon suffers from nutrient pollution due to human impact. Stormwater runoff, faulty sewer systems, and septic tanks, over-fertilized lawns, and excessive development over wetland areas have greatly increased the residual levels of nitrogen and phosphorus in the water.
Algae thrive on the excess nutrients, grows rapidly until it clouds the water, which blocks the sunlight and kills the seagrass beds. The blooming algae also cause a lack of oxygen in the water which in turn kills the marine animals.
DEP's Banana River Lagoon Basin Management Action Plan[5] presents a long-term plan to restore seagrass habitats in the Indian River Lagoon Basin through the reduction of watershed loadings of total nitrogen and total phosphorus.
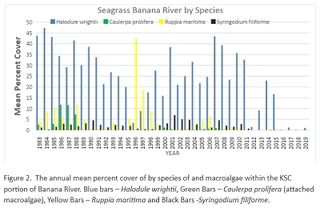
Excerpt from DEP's Banana River Lagoon Progress 2016 Review:
"In 2011, an algal super bloom occurred in the Banana River Lagoon (BRL) and North IRL, with a separate bloom affecting part of the Central IRL. A brown algal bloom affected much of the IRL during 2012. The full impact to seagrasses from these blooms will not be known for a number of years, but there are documented losses of seagrasses in the BRL linked to the blooms. Research is underway to understand the causes of these blooms; however, they appear to be due, in part, to legacy loads in the lagoon from past nutrient discharges. Removing the sources of nutrients from the lagoon’s watershed will help remediate the legacy load."[6]
The Banana River Lagoon Basin Management Action Plan (BMAP) is currently undergoing review and revision for a 2021 adoption.[7]
Article: Banana River Water Quality
Restoration
The 2016 DEP Banana River Lagoon BMAP Progress Report list's many completed and ongoing projects, including stormwater retention systems, stormwater filters, sewer system repairs, and water quality monitoring.[6]
In January 2019 a $2.8 million stormwater and septic conversion project began in Merritt Island. It funded the installation of a new sewer main enabling the conversion of 23 commercial septic tanks and 60 residential septic tanks that were leeching effluent into the lagoon.
The 2019 project also funded the installation of stormwater pipelines that diverted stormwater runoff to retention filtering ponds instead of flowing directly to the river.[8]
Organization
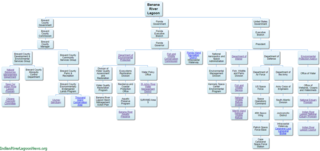
As of 2021 there are approximately fourteen federal, state and county government organizations working within the Banana River lagoon watershed.
Florida's Department of Environmental Protection monitors water quality and sets environmental standards. Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission protects fish, wildlife and habitats, and enforces the law on the water. St. Johns River Water Management District and Brevard County's Save Our Indian River Lagoon Program have worked together on many Banana River restoration projects.
- Interactive chart: Banana River Lagoon Organizational Chart
- Full size image: Media:Banana_River_Organizational_Chart.jpg
Article: Banana River Lagoon Organization
History

Banana River Air Station
Construction of the Banana River Naval Air Station began in December 1939 and the station was commissioned on 1 October 1940.
The station supported seaplane patrol operations during World War II, a blimp squadron which conducted search and rescue along Florida's east coast, a PBM seaplane pilot training program, and an advanced navigation school.
In 1944 the station consisted of 391 officers, 2492 enlisted, and 587 civilians. The number of aircraft present on the base, including F6 Hellcats and O52U Kingfishers, reached a high of 228.

The station continued to operate as a Navy support base for two years after the war, but the installation was deactivated on 1 August 1947.[9]
Patrick Space Force Base
The Navy transferred the station to the Air Force on 1 September 1948 and it was renamed the Joint Long Range Proving Ground (JLRPG). On 1 August 1950, it was renamed Patrick Air Force Base in honor of Major General Mason Patrick.
On December 9, 2020 Patrick Air Force Base was renamed Patrick Space Force Base. Patrick is the headquarters of the 45th Space Wing, the parent organization responsible for operations at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station.[9]

