Nutrient Pollution: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
Stormwater runoff can contain nitrogen and phosphorus pollutants from fertilizers and pet and yard waste. During periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt, some wastewater systems are designed to occasionally overflow and discharge excess untreated sewage directly to nearby streams, rivers, or other water bodies. These discharges are known as combined sewer overflows and are common in many cities nationwide. | Stormwater runoff can contain nitrogen and phosphorus pollutants from fertilizers and pet and yard waste. During periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt, some wastewater systems are designed to occasionally overflow and discharge excess untreated sewage directly to nearby streams, rivers, or other water bodies. These discharges are known as combined sewer overflows and are common in many cities nationwide. | ||
<div class="irlcontentmiddle"> | |||
[[File:stormwater_runoff_infographic.jpg|thumb|left|440px|alt=Residential Stormwater Runoff Pollution Infographic|Residential Stormwater Runoff Pollution Infographic]] | |||
</div> | |||
===Residential Nutrient Pollution=== | ===Residential Nutrient Pollution=== | ||
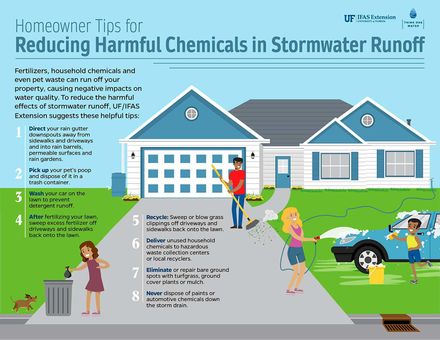
Our homes, through appliances, yards, driveways, and even pets, contribute to nutrient pollution. Roadside storm drains often lead directly to local streams and rivers, so anything that flows into them makes it to local waterways without treatment. | Our homes, through appliances, yards, driveways, and even pets, contribute to nutrient pollution. Roadside storm drains often lead directly to local streams and rivers, so anything that flows into them makes it to local waterways without treatment. | ||
Revision as of 06:39, June 8, 2023
Nitrogen and phosphorus are nutrients that are natural parts of aquatic ecosystems. Nitrogen is also the most abundant element in the air we breathe. Nitrogen and phosphorus support the growth of algae and aquatic plants, which provide food and habitat for fish, shellfish and smaller organisms that live in water.
But when too much nitrogen and phosphorus enter the environment - usually from a wide range of human activities - the air and water can become polluted. Nutrient pollution has impacted many streams, rivers, lakes, bays, and coastal waters for the past several decades, resulting in serious environmental and human health issues, and impacting the economy.
Nutrient Pollution Problem
Too much nitrogen and phosphorus in the water causes algae to grow faster than ecosystems can handle. Significant increases in algae harm water quality, food resources, and habitats, and decrease the oxygen that fish and other aquatic life need to survive. Large growths of algae are called algal blooms and they can severely reduce or eliminate oxygen in the water, leading to illnesses in fish and the death of large numbers of fish. Some algal blooms are harmful to humans because they produce elevated toxins and bacterial growth that can make people sick if they come into contact with polluted water, consume tainted fish or shellfish, or drink contaminated water.
Nutrient pollution in groundwater - which millions of people in the United States use as their drinking water source - can be harmful, even at low levels. Infants are vulnerable to a nitrogen-based compound called nitrates in drinking water. Excess nitrogen in the atmosphere can produce pollutants such as ammonia and ozone, which can impair our ability to breathe, limit visibility, and alter plant growth. When excess nitrogen comes back to earth from the atmosphere, it can harm the health of forests, soils, and waterways.
- Phosphorus - Depending on your soil type, phosphorus from wastewater can be absorbed and retained in the soil. Unabsorbed phosphorus can travel in groundwater toward a water body and become a source of contamination.
- Nitrogen - Some nitrogen may be removed as wastewater flows through the septic system and soil. But the remaining nitrogen can enter the underlying groundwater and flow towards a surface water body. If there are many septic systems in a small area, the nitrogen flowing through groundwater could overload a waterbody, causing eutrophication. Saltwater is more vulnerable to nitrogen pollution.
Where Nutrient Pollution Occurs
Nutrient pollution affects air and water around the country. The impacts of excess nutrients are found in all types of water bodies. Pollutants often enter upstream waters like creeks and streams and then flow into larger water bodies like lakes, rivers, and bays. Excess nitrogen and phosphorus can also travel thousands of miles to coastal areas where the effects of the pollution are felt in the form of massive dead zones, such as those in the Gulf of Mexico and Chesapeake Bay. More than 100,000 miles of rivers and streams, close to 2.5 million acres of lakes, reservoirs, and ponds, and more than 800 square miles of bays and estuaries in the United States have poor water quality because of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution.
Nutrient pollution significantly impacts our nation's coastlines. About two-thirds of the nation's coastal zones and more than one-third of the nation's estuaries showed impairment from nutrient pollution, according to a 2009 EPA report. Nitrogen and phosphorus pollution in rivers, lakes, and streams flows downstream and ultimately enters bays and coastal waters. These coastal ecosystems are often a key part of the local economy and nutrient pollution has a negative impact on commercial fishing, recreation, property values, tourism, and related businesses. Bays and estuaries are more vulnerable to the effects of nutrient pollution because they are often shallow, narrow, or confined, which limits the opportunity for water to circulate oxygen to the plants and animals.
Additionally, nutrients can soak into groundwater, which provides drinking water to millions of Americans, and urban areas across the country have hazy skies and air quality problems related to airborne nitrogen pollution.
Nutrient Pollution Sources and Solutions
The primary sources of excess nitrogen and phosphorus are:
Agriculture Nutrient Pollution
Farmers apply nutrients on their fields in the form of chemical fertilizers and animal manure, which provide crops with the nitrogen and phosphorus necessary to grow and produce the food we eat. However, when nitrogen and phosphorus are not fully utilized by the growing plants, they can be lost from the farm fields and negatively impact air and downstream water quality.
This excess nitrogen and phosphorus can be washed from farm fields and into waterways during rain events and when the snow melts, and can also leach through the soil and into groundwater over time. High levels of nitrogen and phosphorus can cause eutrophication of water bodies. Eutrophication can lead to hypoxic zones, causing fish kills and a decrease in aquatic life. Excess nutrients can cause harmful algal blooms (HABs) in freshwater systems, which not only disrupt wildlife but can also produce toxins harmful to humans.
Fertilized soils, as well as livestock operations, are also vulnerable to nutrient losses to the air. Nitrogen can be lost from farm fields in the form of gaseous, nitrogen-based compounds, like ammonia and nitrogen oxides. Ammonia can be harmful to aquatic life if large amounts are deposited from the atmosphere to surface waters.
Stormwater Nutrient Pollution
In undeveloped areas precipitation typically soaks into the ground. However, when buildings, parking lots, roads, and other hard surfaces are added to the landscape, the ground cannot absorb the water. Water from rain or snowstorms, known as stormwater, flows over streets, parking lots, and roofs and into a water body or storm drain. Urban and suburban areas produce much more stormwater runoff due to the high amount of paved and hard surfaces.
Stormwater runoff can contain nitrogen and phosphorus pollutants from fertilizers and pet and yard waste. During periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt, some wastewater systems are designed to occasionally overflow and discharge excess untreated sewage directly to nearby streams, rivers, or other water bodies. These discharges are known as combined sewer overflows and are common in many cities nationwide.
Residential Nutrient Pollution
Our homes, through appliances, yards, driveways, and even pets, contribute to nutrient pollution. Roadside storm drains often lead directly to local streams and rivers, so anything that flows into them makes it to local waterways without treatment.
Residential areas can be a significant source of excess nitrogen and phosphorus pollution from fertilizers. Over-fertilizing and overwatering a yard is a common practice among homeowners and landscaping services and can lead to fertilizer being washed away more easily. Additionally, pet waste contributes to nitrogen, phosphorus, parasites, and bacteria to water bodies when it is not disposed of properly. Pet waste that is not properly disposed of can lead to conditions in local water bodies that are unsafe for human recreation.
There are also sources of nutrient pollution inside our homes. Many laundry, dish, and car washing soaps contain a form of phosphorus called phosphates, which are carried from our homes into the water system through our drains. We also add excess nitrogen to the atmosphere through the use of electricity in our homes. Most of our electricity comes from the burning of fossil fuels, which release pollutants into the environment.
Fossil Fuel Nutrient Pollution
Airborne nitrogen pollution affects not only the quality of the air we breathe but also the land and the water. Nitrogen is the most abundant element in the air and is essential to plant and animal life. Sources of nitrogen from human activities, such as electric power generation, industry, transportation, and agriculture, can upset the natural balance of nitrogen in the environment.
When fossil fuels are burned, they release nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere, which contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain. The most common nitrogen-related compounds emitted into the air by human activities are collectively referred to as nitrogen oxides. Ammonia is another nitrogen compound emitted to the air, primarily from agricultural activities, but also from fossil fuels. Most of the nitrogen oxides released in the U.S. due to human activity are from the burning of fossil fuels associated with transportation and industry.
Major sources of nitrogen oxide emissions include:
- Cars and trucks
- Coal-fired power plants
- Large industrial operations
- Ships and airplanes
The presence of excess nitrogen in the atmosphere in the form of nitrogen oxides or ammonia is deposited back onto land, where it washes into nearby water bodies. These excess nutrients contribute to pollution, harmful algal blooms and oxygen-deprived aquatic zones. Excess ammonia and low pH in these areas are toxic to aquatic organisms and affect their survival.
Nutrient Pollution Effects
The presence of excess nutrients in air and water can affect human health, the environment, and the economy. Federal, state, and local governments spend billions of dollars per year to minimize these effects.
Human Health Effects
Excess nutrients and harmful algal blooms create toxins and compounds in water that pose danger for human health. There are several ways that people (and pets) can be exposed to these compounds.
Direct exposure to toxic algae
Drinking water can be a source of exposure to chemicals caused by nutrient pollution. Drinking, accidentally swallowing or swimming in water affected by a harmful algal bloom can cause serious health problems including:
- Rashes
- Stomach or liver illness
- Respiratory problems
- Neurological effects
Nitrates in drinking water
Nitrate, a compound found in fertilizer, can enter drinking water in agricultural areas. A 2010 report on nutrients in ground and surface water by the U.S. Geological Survey found that nitrates were too high in 64 percent of shallow monitoring wells in agricultural and urban areas.
Infants are more susceptible to the health effects posed by nitrates, which can be serious and sometimes fatal.
Byproducts of water treatment
Stormwater runoff can carry nutrients directly into rivers, lakes and reservoirs, which serve as sources of drinking water for many people. When disinfectants used to treat drinking water react with toxic algae, harmful chemicals called dioxins can be created. These byproducts have been linked to serious health problems, including reproductive and developmental health risks.
Nutrient Pollution Environmental Effects
Nutrient pollution fuels the growth of harmful algal blooms which have negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
Direct exposure to algae
Harmful algal blooms sometimes create toxins that are detrimental to fish and other animals. After being consumed by small fish and shellfish, these toxins move up the food chain and can impact larger animals like sea lions, turtles, dolphins, birds and manatees.
Even if algal blooms are not toxic, they can negatively impact aquatic life by blocking out sunlight and clogging fish gills.
Dead zones and hypoxia
Nutrient pollution can create dead zones - areas in water with little or no oxygen - where aquatic life cannot survive. Also known as hypoxia, these areas are caused by algal blooms consuming oxygen as they die and decompose. Aquatic animals - particularly young fish and seafloor dwellers like crabs and clams - must leave the affected area to survive.
Over 166 dead zones have been documented nationwide, affecting water bodies like the Chesapeake Bay and the Gulf of Mexico. The Gulf of Mexico's dead zone is the largest in the United States, measured to be 5,840 square miles in 2013. It occurs every summer because of nutrient pollution from the Mississippi River Basin, an area that drains 31 upstream states. The Mississippi River/Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Task Force coordinates nutrient management in this area.
Acid rain
Acid rain, caused by nutrient pollution in the air, damages lakes, streams, estuaries, forests and grasslands across the country.
Air pollution
Airborne nitrogen compounds like nitrogen oxides contribute to the formation of other air pollutants such as ground-level ozone, a component of smog that can restrict visibility. Wind and weather can carry ozone many miles from urban to rural areas. Ozone pollution can damage trees and harm the appearance of vegetation and scenic areas.
Nutrient Pollution Economic Effects
Nutrient pollution has diverse and far-reaching effects on the U.S. economy, impacting tourism, property values, commercial fishing, recreational businesses, and many other sectors that depend on clean water.
Drinking water costs
Nitrates and algal blooms in drinking water sources can drastically increase treatment costs. For example, nitrate-removal systems in Minnesota caused supply costs to rise from 5-10 cents per 1000 gallons to over $4 per 1000 gallons.
It can also cost billions of dollars to clean up polluted water bodies. Every dollar spent on protecting sources of drinking water saves in water treatment costs.
Tourism losses
The tourism industry loses close to $1 billion each year, mostly through losses in fishing and boating activities, as a result of water bodies that have been affected by nutrient pollution and harmful algal blooms.
Airborne nutrient pollution can also affect visibility at popular outdoor destinations like national parks. This kind of pollution can also damage buildings and other structures, especially those made of marble and limestone.
Commercial fishing and shellfish losses
Fishing and shellfish industries are hurt by harmful algal blooms that kill fish and contaminate shellfish. Annual losses to these industries from nutrient pollution are estimated to be in the tens of millions of dollars.
Real estate losses
Clean water can raise the value of a nearby home by up to 25 percent. Waterfront property values can decline because of the unpleasant sight and odor of algal blooms.