Glossary:Eutrophication: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{definition | {{definition | ||
|Term=eutrophication | |Term=eutrophication | ||
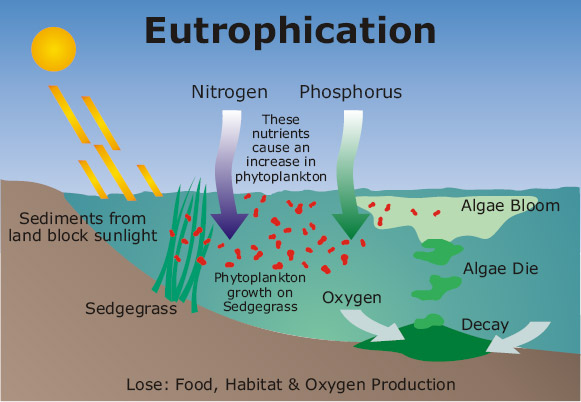
|Definition=process by which large additions of nutrients causes an overgrowth of algae and subsequent depletion of oxygen. | |||
|SourceURL=https://coast.noaa.gov/estuaries/estuary-resources/glossary.html | |||
|Type=noun | |Type=noun | ||
|Pronunciation=eu·troph·i·ca·tion | |Pronunciation=eu·troph·i·ca·tion / yo͞oˌträfəˈkāSH(ə)n | ||
|AudioFile=glossary eutrophication.mp3 | |AudioFile=glossary eutrophication.mp3 | ||
| | |ImageFile=Glossary eutrophication.jpeg | ||
|Poster=Admin | |Poster=Admin | ||
|Postdate=20191107193329 | |Postdate=20191107193329 | ||
|TermID= | |TermID=E | ||
}} | }} | ||
<div class="irlcontentmiddle"> | <div class="irlcontentmiddle"> | ||
Latest revision as of 20:56, December 18, 2020
Eutrophication in the Indian River Lagoon
Eutrophication is caused by excessive nitrogen and/or phosphorous polluting a water body, where it results in a dense growth of algae, followed by the death of animal life resulting from oxygen depletion. Sadly, in many subtropical estuaries such as the IRL, we have documented “phase shifts” from seagrass to macroalgae to toxic phytoplankton blooms and cascading impacts on the lagoon’s biota.
Phytoplankton are single-celled algae that thrive in the water column. Healthy estuaries produce “good” species of phytoplankton that turn sunlight into energy and in turn feed organisms such as oysters and important consumers, such as the forage fish called menhaden. Eutrophic, or, in the case of the IRL, hypereutrophic estuaries produce toxic phytoplankton, including those that cause brown and red tides, as well as cyanobacteria blooms. Their toxins reduce the growth of other phytoplankton, block sunlight to benthic plants, and release toxins into the water and air.
From Sewage on the Move by Dr. Peter Barile, Senior Scientist at Marine Research & Consulting Inc.